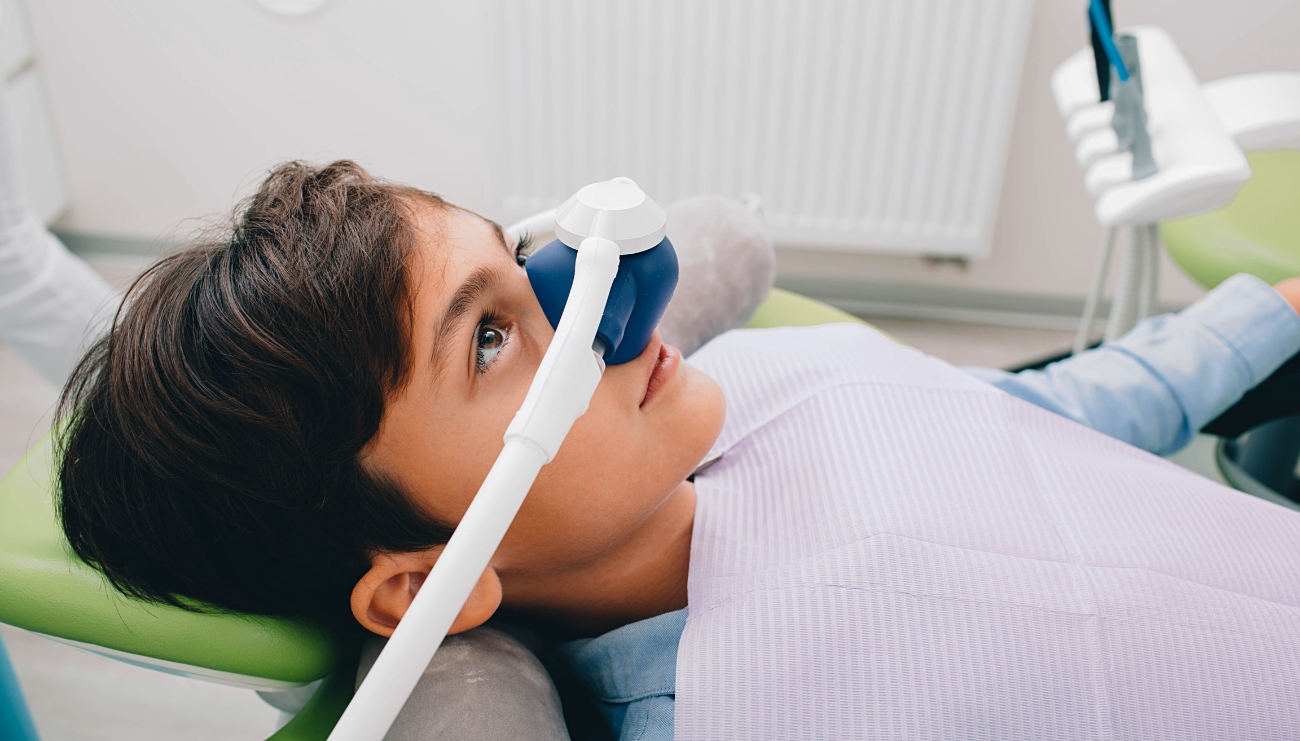
General Dentistry at Vivaldi Smile Artisans
What is “happy gas”?
“Happy gas” is a colloquial term for nitrous oxide (N2O), also known as laughing gas. Nitrous oxide is a colourless and odorless gas that has both anaesthetic and analgesic properties, meaning it can induce mild sedation and reduce pain (conscious sedation). In medical and dental settings, nitrous oxide is commonly used as a mild sedative and analgesic during certain procedures and it can be particularly beneficial for anxious patients and children.
It is typically administered through a nosepiece, allowing the patient to inhale a controlled mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen. The nitrous oxide concentration is carefully regulated to achieve the desired level of sedation and pain relief while ensuring the patient’s safety.
Once the procedure is finished, the patient receives pure oxygen for about 5 minutes and there is no residual effect, which allows going back to normal activities straight after the appointment.
How does it work?
When inhaled, nitrous oxide enters the lungs and is absorbed into the bloodstream. It then travels to the brain, where it affects the central nervous system. Nitrous oxide interacts with various receptors in the brain that play a role in pain perception and mood regulation.
The primary mechanism of action of nitrous oxide is believed to be the activation of the opioid receptors, which results in a release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers. This can lead to a sense of happiness, relaxation, and decreased sensitivity to pain. Nitrous oxide also affects the release of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which contributes to its pleasurable effects.
Additionally, nitrous oxide has a depressant effect on the central nervous system, causing sedation and a feeling of calmness. It slows down the transmission of nerve impulses, reducing the perception of pain and inducing a sense of well-being.
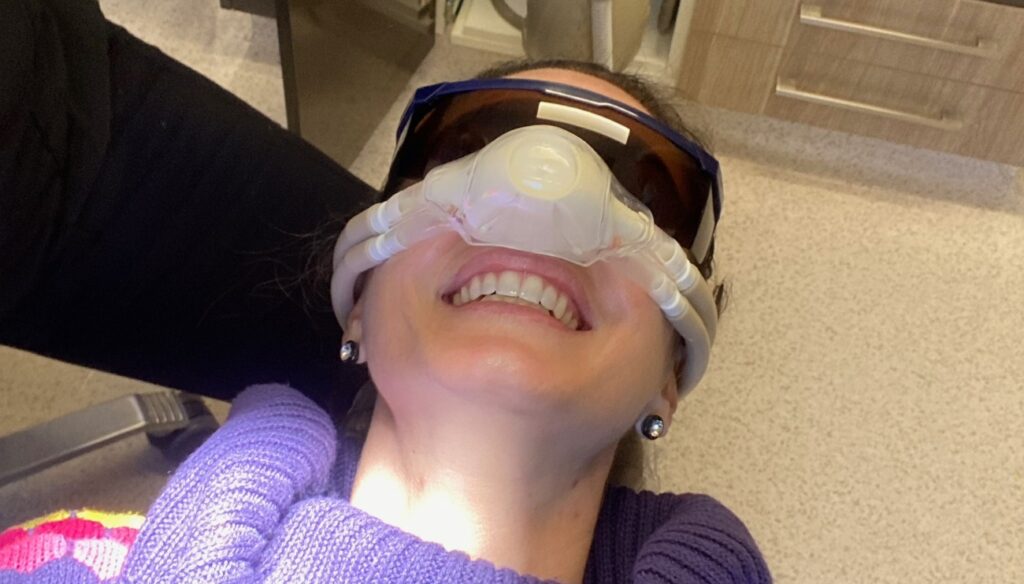

How does it work?
When inhaled, nitrous oxide enters the lungs and is absorbed into the bloodstream. It then travels to the brain, where it affects the central nervous system. Nitrous oxide interacts with various receptors in the brain that play a role in pain perception and mood regulation.
The primary mechanism of action of nitrous oxide is believed to be the activation of the opioid receptors, which results in a release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers. This can lead to a sense of happiness, relaxation, and decreased sensitivity to pain. Nitrous oxide also affects the release of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which contributes to its pleasurable effects.
Additionally, nitrous oxide has a depressant effect on the central nervous system, causing sedation and a feeling of calmness. It slows down the transmission of nerve impulses, reducing the perception of pain and inducing a sense of well-being.
Are there any side effects?
While it is generally considered safe when administered by a trained professional, with the correct concentration, there are potential side effects associated with its use. Some of the possible side effects of happy gas include: Nausea: This is the most common side effect, especially when high concentrations of nitrous oxide are used or when it is administered on an empty stomach. Dizziness: Nitrous oxide can cause a temporary feeling of dizziness, particularly when transitioning between sedation and wakefulness. Headache: Some individuals may experience a mild headache after the administration of nitrous oxide. This side effect is usually temporary and resolves on its own. Fatigue: After the use of nitrous oxide, some people may feel tired or sleepy for a short period. It’s important to note that these side effects are generally mild and short-lived, and the vast majority of people tolerate nitrous oxide well.If you’re ready to start smiling more, come and visit us in our Sydney CBD dental clinic


